Energy Storage Systemsand Microgrids
Solutions for Energy Storage
A BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) is a system that uses batteries to store electrical energy and releases it when needed, improving the reliability, flexibility, and efficiency of energy systems.
System Use
- Stores energy produced from renewable sources or the electrical grid.
- Releases energy when needed (e.g., demand peaks, blackouts).
- Stabilizes the grid by supporting frequency and voltage.
- Optimizes consumption, reducing costs and waste.
Main components
- Batteries: lithium, lead-acid, sodium, or other technologies.
- Inverter: converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) and vice versa.
- DC/DC Converters (optional): regulate battery voltage.
- Control System: for monitoring, automation, and safety.
- Auxiliary Systems: cooling, fire protection, ventilation.
Applications
- In electrical grids (utility-scale) to balance production.
- In photovoltaic or wind plants to make renewable energy more predictable.
- In microgrids or industrial plants to ensure backup power.
- In residential and commercial settings for self-consumption and cost reduction.
ENERGY POWER CONVERSION
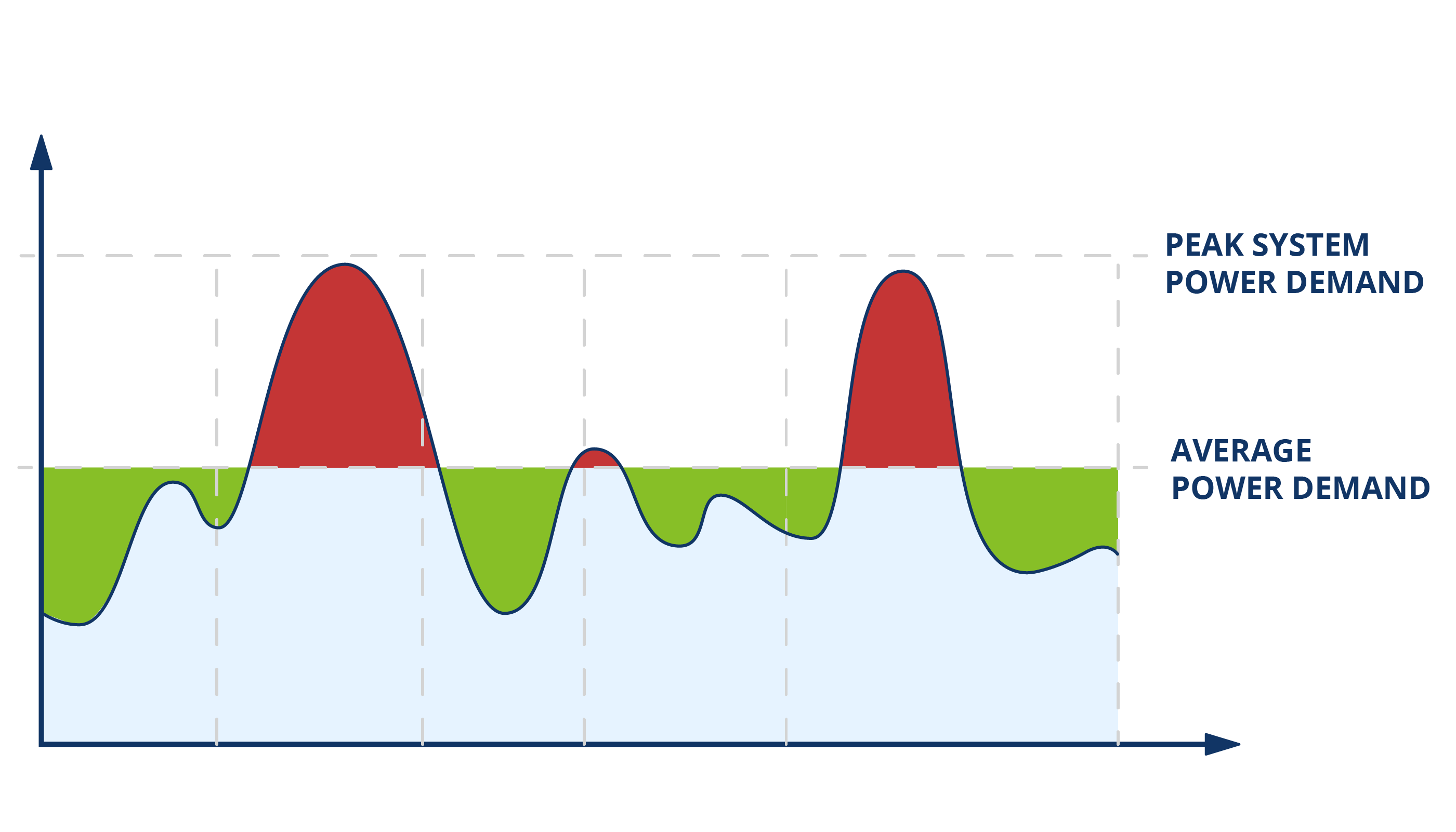
Peak Shaving:
Peak shaving is an energy demand management strategy aimed at reducing consumption peaks during high-demand periods. During these times, energy demand reaches high levels, putting pressure on the electrical grid. The goal of peak shaving is to lower these peaks, avoiding both grid overload and the need to activate additional energy generation resources.
There are several techniques used to implement peak shaving. One of the most common involves energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store excess energy during low-demand periods and release it during peaks. This approach helps reduce the load on the electrical grid.
Other techniques include load management, incentive programs to shift consumption to off-peak hours, adoption of more efficient energy technologies, and use of alternative renewable energy sources.
The goal of peak shaving is to efficiently balance energy demand and supply, reducing additional costs and minimizing the environmental impact caused by energy generation during high-demand periods.
Load sharing:
Load sharing is a technique used in distributed generation systems to evenly distribute the workload across all nodes, ensuring that no node remains idle and that the system can efficiently handle the demand.
This approach helps maintain system performance and reliability by preventing any single node from becoming overloaded and creating a bottleneck.
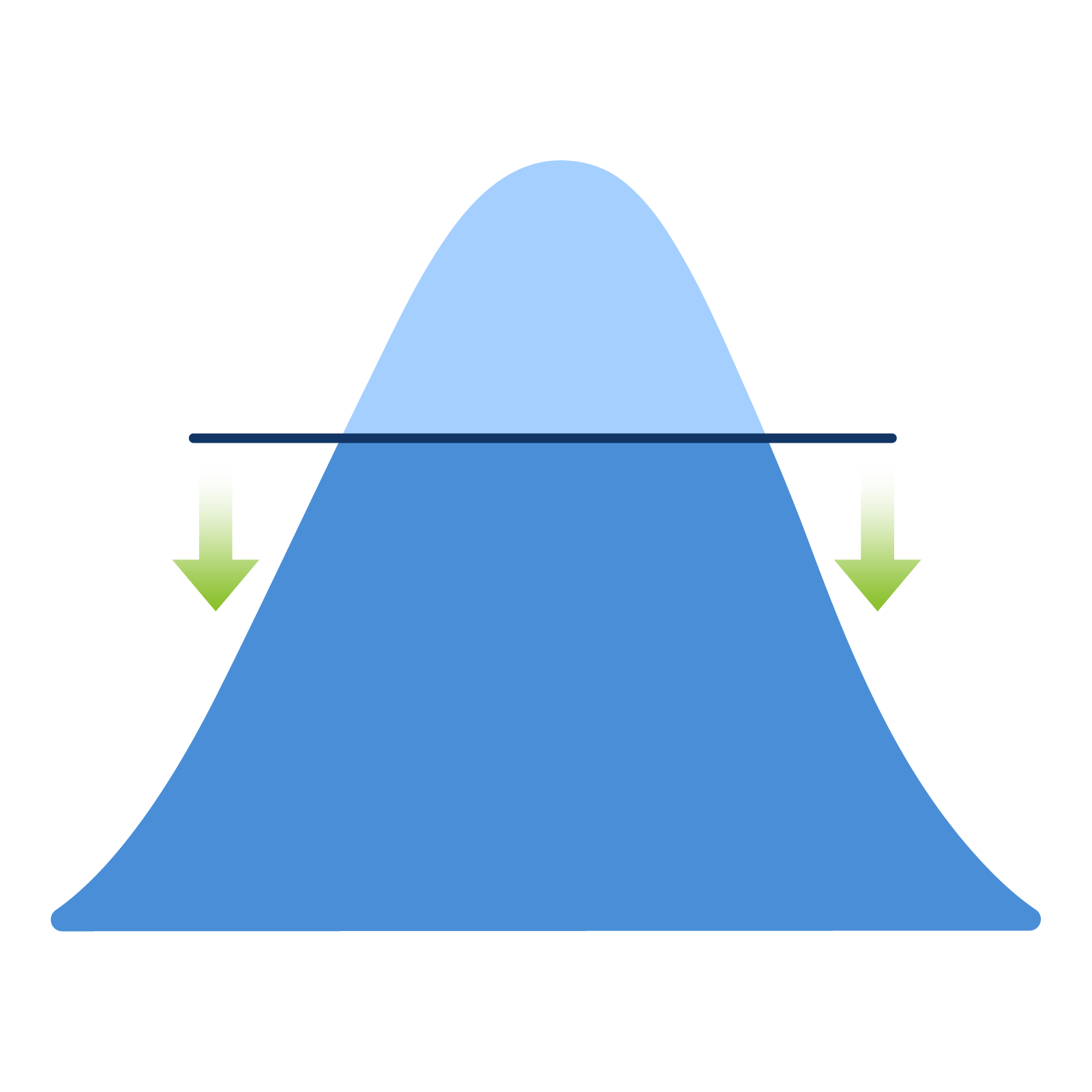
PEAK SHAVING
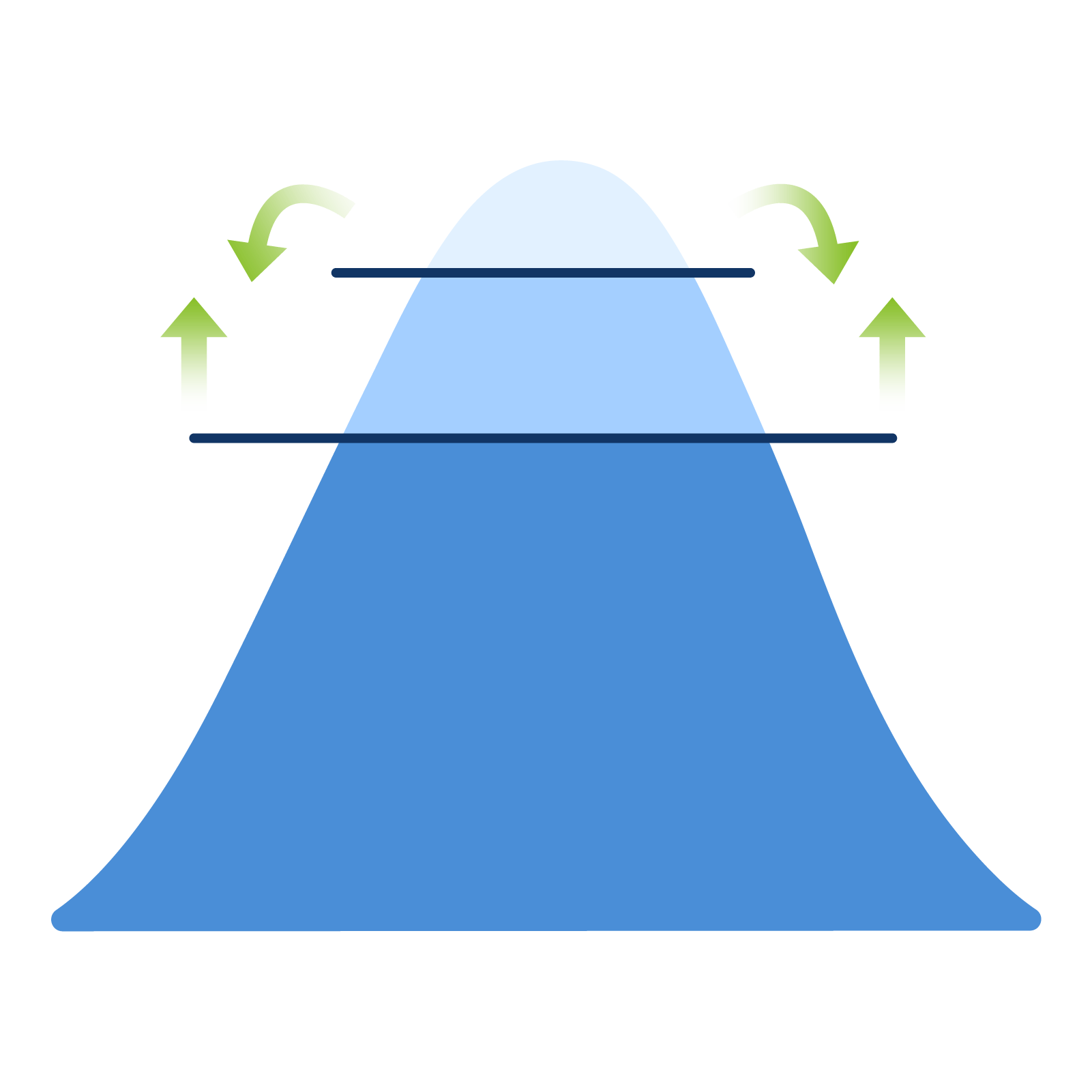
LOAD SHIFTING
Microgrid:
This term refers to a sub-network capable of operating either in parallel with the grid or independently, using distributed generation and storage systems to power the loads. In this case, bidirectional generation and storage systems must be capable of operating both in island mode (VSI – Voltage Source Inverter) and in grid-parallel mode (CSI – Current Source Inverter).
- Grid voltage anomaly detection with preemptive disconnection and transition to VSI mode: This prevents malfunctions related to grid oscillations.
- VSI/CSI transition management: Enables seamless switching between VSI and CSI to synchronize the microgrid and allow reconnection to the main grid without service interruption.
- Parallel operation of the storage system with the grid or other generation sources with possible power sharing: This function is used in hybrid systems where, for example, a BESS (Battery Energy Storage System) can operate in parallel with a genset.
- Droop control: A function that ensures proper interaction between multiple distributed generation systems operating on the same grid.
- Black start: A function that enables the generation of a ramped voltage in VSI mode, allowing gradual magnetization of inductive loads (such as transformers).
Green Energy Generationand Power Quality
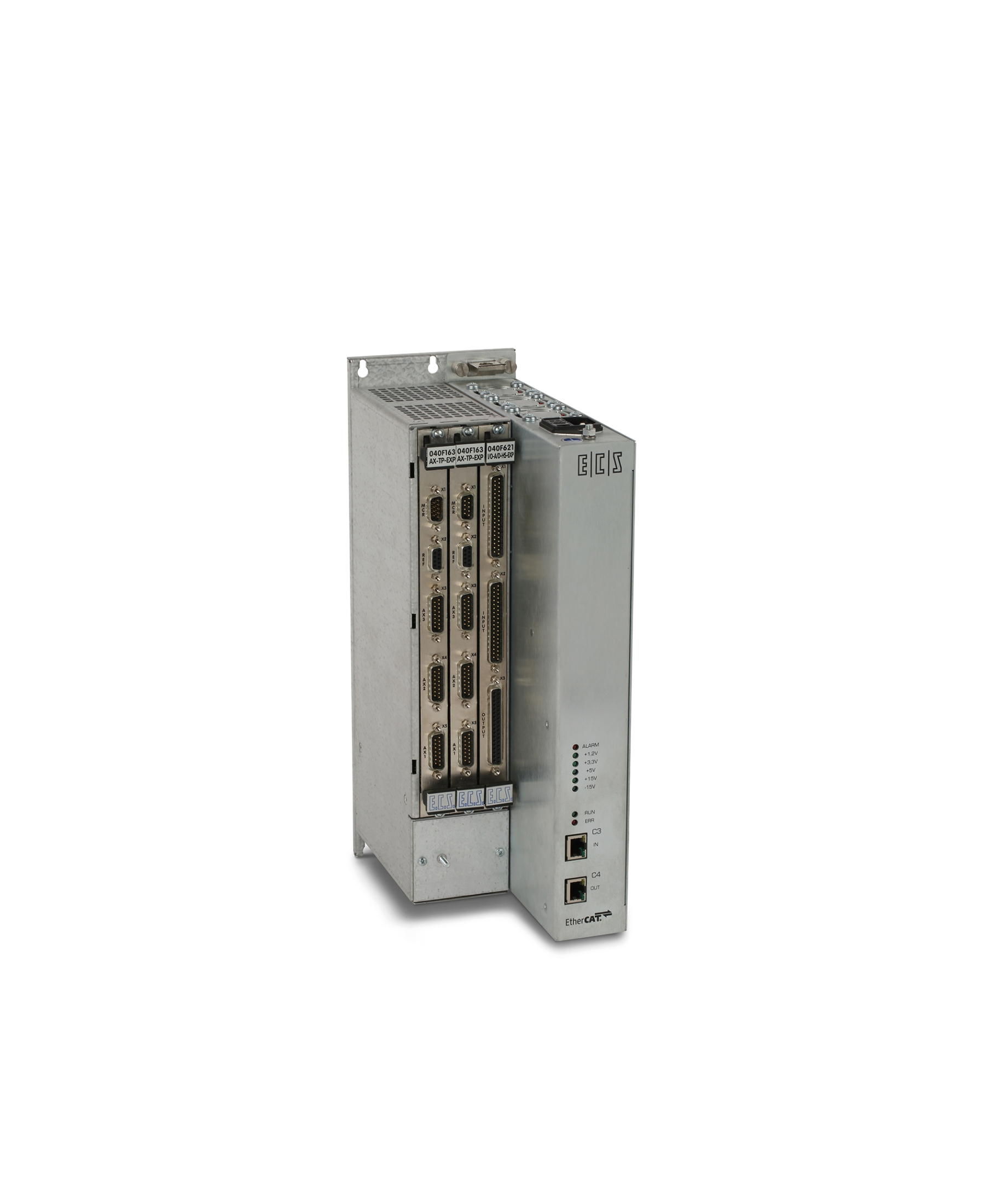
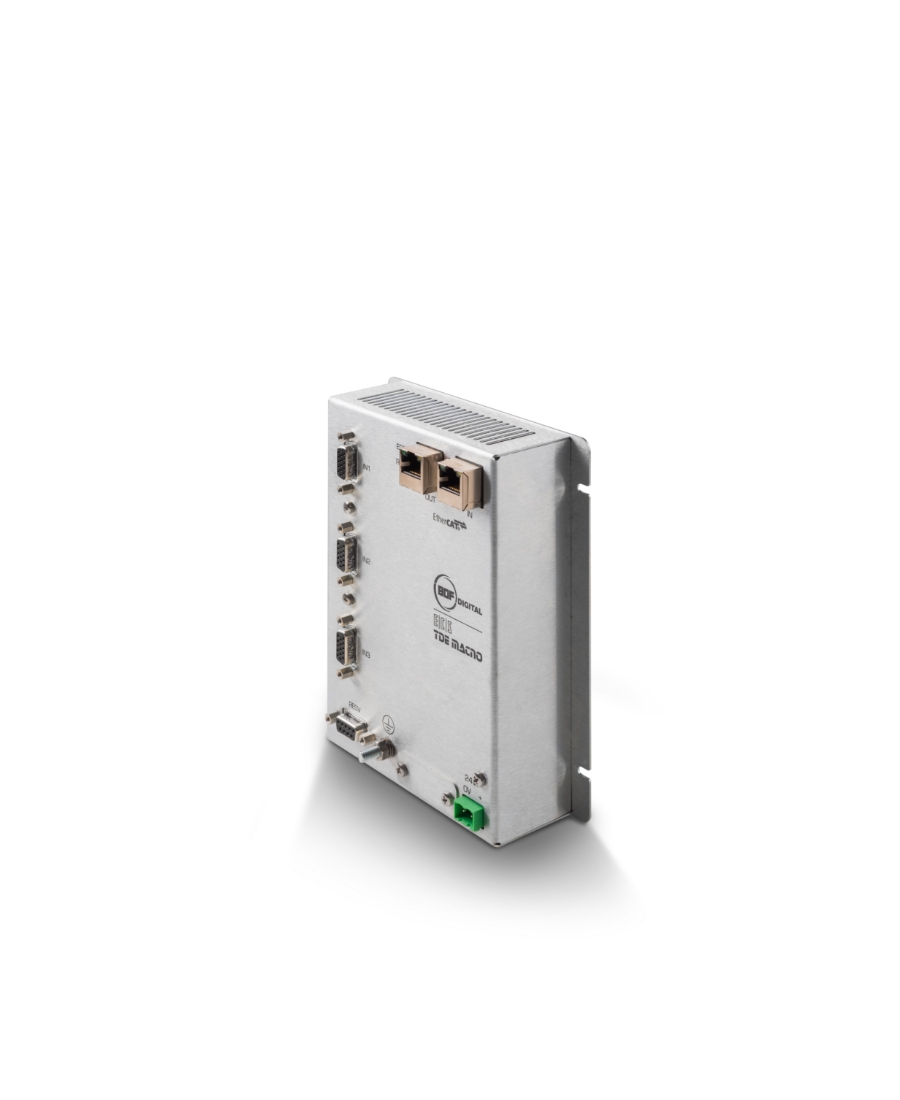
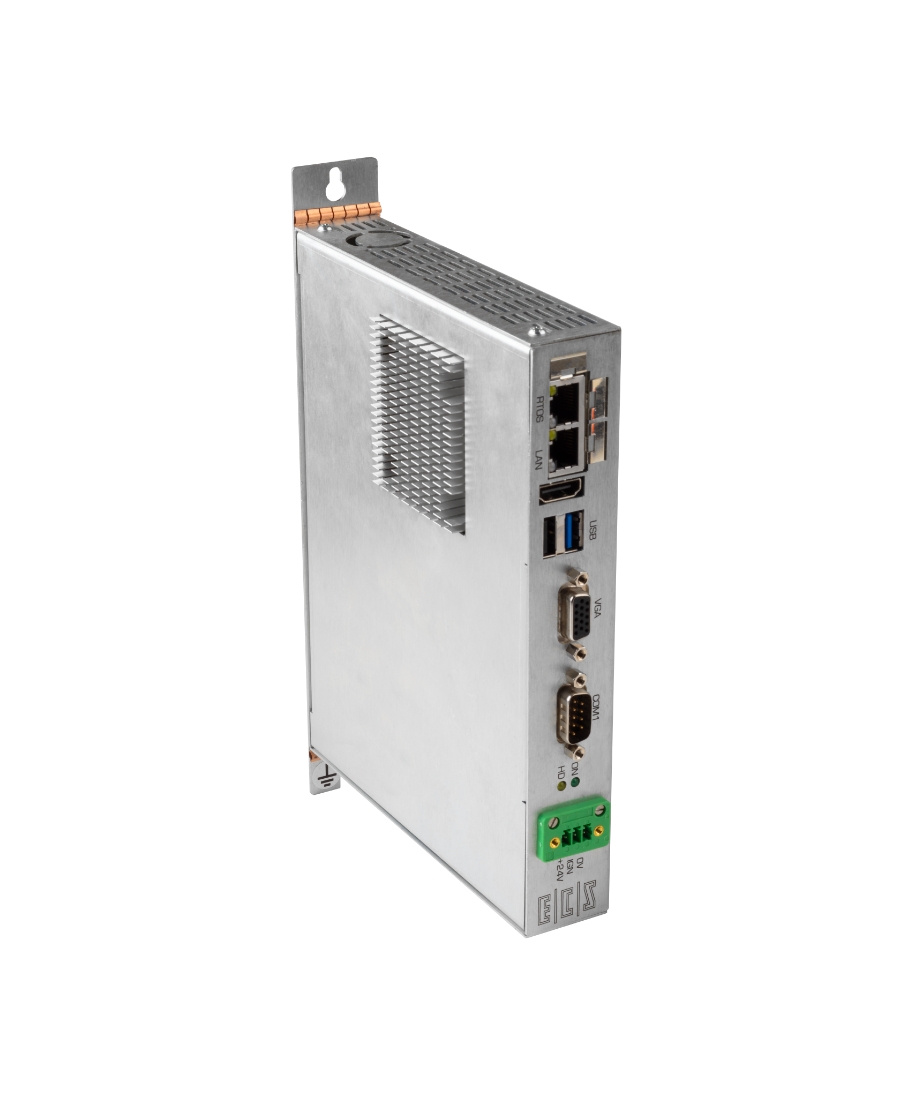
RELATED PRODUCTS
Case History
Contact us!
Haven’t found what you were looking for? Contact us!